What is vegetable oil substitute and the best substitute is the topic of this article. Vegetable oils can be derived from sources like soybeans, sunflowers, olives, and coconuts. Additionally, vegetable oils have diverse uses beyond cooking, such as in biodiesel production, cosmetics, and as components in various industrial products like soaps and paints.

Table of Contents
Different types of vegetable oil.

Vegetable oils come in a wide variety of forms, such as:
Olive oil
Extracted from olives, used in cooking and cosmetics
Coconut oil
Extracted from coconuts, used in cooking, medicine and industry
Soybean oil
Extracted from soybeans, one of the most widely produced vegetable oils
Sunflower oil
Extracted from sunflower seeds, a common cooking oil
Corn oil
Extracted from corn, one of the principal oils sold as salad and cooking oil
Peanut oil
Extracted from peanuts, used for frying due to its high smoke point
Canola oil
Extracted from rapeseed, the most widely consumed cooking oil worldwide
Cotton Seed oil
Extracted from cotton seeds, used as a cooking oil
Palm oil
Extracted from the fruit of oil palms, the most widely produced tropical oil
Sesame oil
Extracted from sesame seeds, used as a cooking oil
Avocado oil
Extracted from avocados, used in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals
Grape Seed oil
Extracted from grape seeds, used in cooking and cosmetics
Other less common vegetable oils include almond oil, apricot oil, argan oil, babassu oil, ben oil, and many more. Vegetable oils are primarily composed of triglycerides and are typically liquid at room temperature.



Health risks associated with consuming vegetable oil.
Consuming vegetable oil has been linked to several health risks, including:
Cardiovascular Disease:
Heated vegetable oil consumption may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease by affecting serum lipid profiles and blood pressure
Unhealthy Gut:
High consumption of soybean oil has been linked to obesity, diabetes, and potentially autism, Alzheimer’s disease, anxiety, and depression
Skin Cancer:
Vegetable oils are rich in omega 6, which can cause accelerated growth of cancer cells, blood clotting, and increased inflammation in the body. Unhealthy fats can also cause skin cancer if they enter the skin.
Inflammation and Pain:
Oxidized oils can cause inflammation and pain in the body, even after the oil looks and smells fine
Cell Mutations and Artery Clogging:
Polyunsaturated fats, which are not intended for human consumption, are abundant in vegetable oils. These fats can cause mutations in the cells and clog the arteries
Imbalance of Omega 3 and 6:
Heart problems, autoimmune illnesses, neurological diseases, and possibly cancer are caused by an imbalance between omega 3 and 6.
Conversion of Good Cholesterol to Bad:
Vegetable oils may convert the good cholesterol (HDL) present in the body into bad cholesterol (LDL)
Genetically modified grains are used to make a variety of vegetable oils, most notably canola, soybean, and corn (GMO). These are typically biologically engineered and heavily treated with pesticides, rendering them unfit for human consumption.
However, it’s important to note that not all vegetable oils are unhealthy. Some oils, like olive oil, are rich in unsaturated fats and low in saturated fats, making them a healthier choice. Additionally, the health risks associated with vegetable oils can be minimized by choosing vegetable oil substitute that are more resistant to oxidation, reading labels for trans fat content, avoiding high heat cooking, and limiting oil consumption
What is vegetable oil Substitute?
A common substitute for vegetable oil in cooking and baking is unsweetened applesauce. Other alternatives include mashed fruit like bananas, pears, and prunes, as well as pureed fruit. Additionally, yogurt, ghee, margarine, mayonnaise, and even mashed avocado can be used as substitutes for vegetable oil in various recipes. These alternatives can help maintain moisture and texture in baked goods while reducing the reliance on traditional oils
To explain the best vegetable oil substitutes step by step, here are some common alternatives and how they can be used:


Canola, Corn, Palm, and Soybean Oil:
These oils are often used interchangeably with vegetable oil in recipes that require high-heat cooking or frying.
Peanut Oil:
Peanut oil is similar to vegetable oil and is particularly suitable for frying due to its high smoke point and neutral flavor.
Olive Oil:
Regular olive oil can be used for frying, while extra-virgin olive oil is better suited for salad dressings and finishing oils due to its cold-press extraction process. It is taken as the best vegetable oil substitute at present.
Coconut Oil:
Coconut oil is a versatile substitute for vegetable oil in both frying and baking, but it has a slightly coconutty flavor and solidifies at cooler temperatures. it is one of the best vegetable oil substitute.
Butter:
Butter can add richness to dishes and is a great vegetable oil substitute in baking, but it should not be used for deep-frying due to its low smoke point.
Applesauce:
Applesauce is an excellent substitute for vegetable oil in baking, adding moisture and reducing the overall fat content of the recipe.
Greek Yogurt:
Greek yogurt can be used as a substitute for vegetable oil in baking, providing moisture, richness, and a tangy flavor.
Mayonnaise:
Mayonnaise is a useful substitute for vegetable oil in baking, resulting in moist and rich baked goods.
Avocado Oil:
Avocado oil is a healthy alternative to vegetable oil, rich in monounsaturated fats and suitable for high-heat cooking and salad dressings. it is one of the best vegetable oil substitute.
Sunflower Oil:
Sunflower oil is light and neutral-flavored oil that can be used as a substitute for vegetable oil in cooking and baking.
Grape seed Oil:
Grape seed oil is versatile oil with a high smoke point, making it suitable for frying and sautéing as a substitute for vegetable oil.
Almond Oil:
Almond oil is a flavorful and nutritious substitute for vegetable oil in baking, adding a nutty taste to dishes.
Flax seed Oil:
Flax seed oil is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids and can be used as a vegetable oil substitute in salad dressings and cold dishes.
Sesame Oil:
Sesame oil adds a distinct nutty flavor to dishes and can be used as a vegetable oil substitute in stir-fries and Asian-inspired recipes.
Hazelnut Oil:
Hazelnut oil is a flavorful option for baking and salad dressings, providing a rich and nutty taste as a vegetable oil substitute.
Walnut Oil:
Walnut oil is delicate oil with a nutty flavor, ideal for drizzling over salads or using as a vegetable oil substitute in baking.
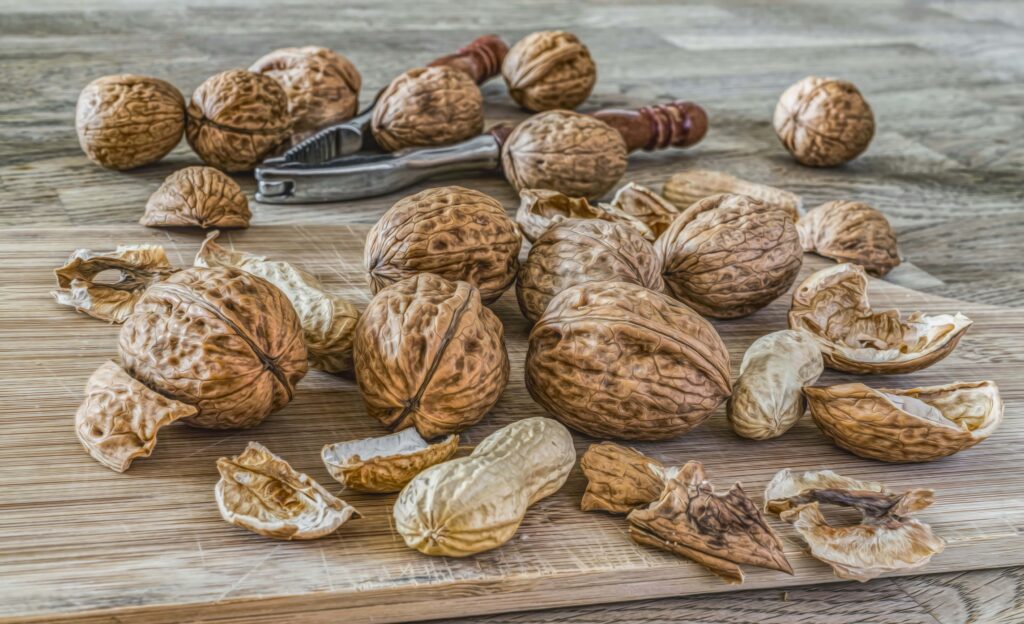
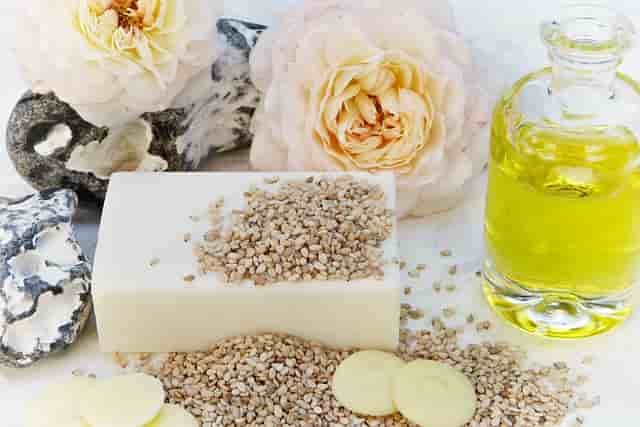


These vegetable oil substitute can be used in various recipes depending on the desired outcome, whether for frying, baking, or adding moisture and flavor to dishes. Each substitute has its unique characteristics, making them suitable for different cooking and baking needs.
These additional options offer a variety of flavors and nutritional benefits, allowing for versatility in cooking and baking while serving as alternatives to traditional vegetable oils.
Nutritional differences between vegetable oil and its substitutes.
The nutritional differences between vegetable oil and its substitutes vary depending on the specific type of oil or substitute used. Here are some key points:
Vegetable Oil:
- Generally rich in mono- and polyunsaturated fats.
- May contain unhealthy trans fats if partially hydrogenated
- Often processed with chemical solvents
Olive Oil:
- High in monounsaturated fats, which may help lower heart disease risk.
- Extra-virgin olive oil is minimally processed and retains more nutrients Has a stronger flavor that may not be suitable for all recipes.
Coconut Oil:
- Contains saturated fats, but some may have neutral effects on cholesterol.
- Provides lauric acid, which may raise “good” HDL cholesterol Solid at room temperature, so it needs to be melted for some recipes.
Avocado Oil:
- High in monounsaturated fats and vitamin E.
- Has a high smoke point suitable for high-heat cooking.
- More expensive than other options.
Applesauce:
- Low in calories and fat, making it a healthier substitute in baked goods.
- Adds moisture and sweetness to recipes.
- Alters the texture of baked goods, making them more cake-like.
Greek Yogurt:
- Provides protein and calcium.
- Gives baked products more moisture and richness.
- Imparts a tangy flavor The choice of substitute depends on the recipe, cooking method, and personal preferences.
Healthier options like olive oil, avocado oil, and coconut oil can be used in place of vegetable oil, while applesauce and Greek yogurt work well in baking to reduce fat and calories.
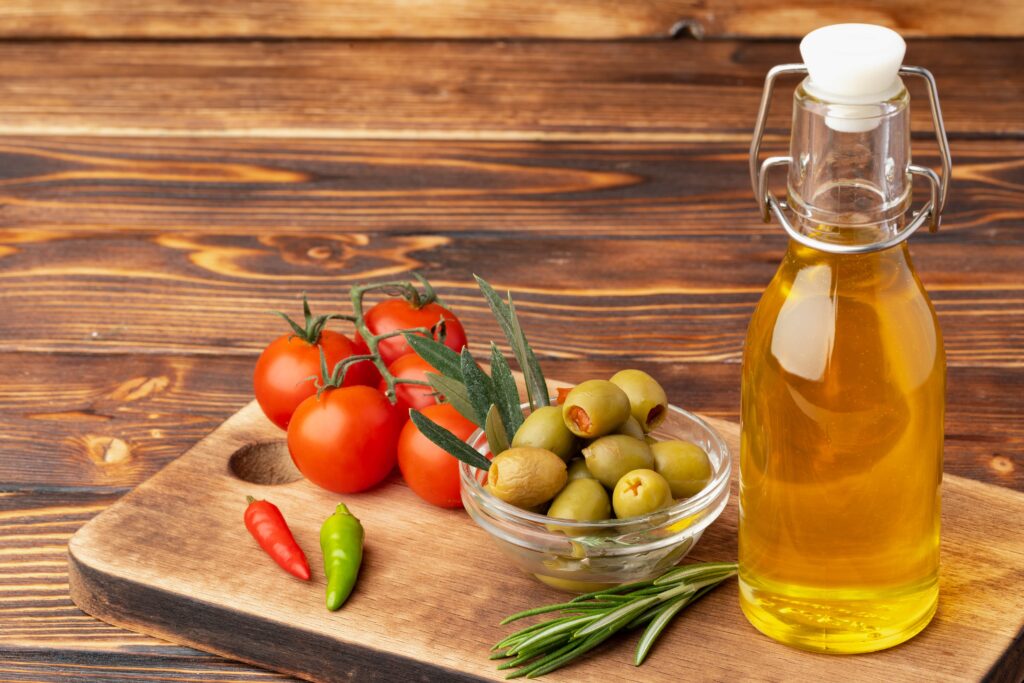


Which vegetable oil substitute is the Healthiest?
The healthiest vegetable oil substitutes are:
Olive Oil:
- Extra virgin olive oil is minimally processed and retains more nutrients
- High in monounsaturated fats that may help lower heart disease risk. Best used in dressings, marinades, and for sautéing at low to medium heat
Avocado Oil:
- High in monounsaturated fats and vitamin E
- Has a high smoke point suitable for high-heat cooking
- More expensive than other options
Coconut Oil:
- Contains lauric acid that may raise “good” HDL cholesterol
- Withstands high heat well for cooking and baking Solid at room temperature, so it needs to be melted for some recipes.
Applesauce:
- Low in calories and fat, making it a healthier substitute in baked goods
- Adds moisture and sweetness to recipes Alters the texture of baked goods, making them more cake-like.


While these substitutes offer health benefits compared to vegetable oil, it’s important to consume them in moderation as they are still high in calories and fat. The choice ultimately depends on the recipe, cooking method, and personal preferences.
Contact Us for any Question related to this Article.
Frequently Asked Questions.
What is vegetable oil?
Vegetable oil refers to oils extracted from seeds, fruits, nuts, or other parts of plants. These oils are primarily used in cooking, food preparation, and various industrial applications due to their liquid form at room temperature.
What are the different types of vegetable oils?
There are various types of vegetable oils, including olive oil, coconut oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil, corn oil, peanut oil, canola oil, palm oil, sesame oil, avocado oil, and more. Each type has unique characteristics and uses in cooking and other applications.
What is the health risks associated with consuming vegetable oil?
Consuming vegetable oil has been linked to health risks such as cardiovascular disease, unhealthy gut issues, skin cancer, inflammation, cell mutations, and an imbalance of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Choosing healthier alternatives and moderating consumption can help mitigate these risks.
What is a good substitute for vegetable oil?
Unsweetened applesauce, mashed fruit like bananas, pears, and prunes, yogurt, ghee, margarine, mayonnaise, and mashed avocado are some common substitutes for vegetable oil in cooking and baking. These alternatives can help maintain moisture and texture in dishes while reducing reliance on traditional oils.
What are the nutritional differences between vegetable oil and its substitutes?
Vegetable oils like olive oil, coconut oil, and avocado oil offer different nutritional profiles compared to traditional vegetable oil. For example, olive oil is high in monounsaturated fats, while coconut oil contains saturated fats. Substitutes like applesauce and Greek yogurt provide lower fat and calorie content in recipes.
Which vegetable oil substitute is the healthiest?
Among vegetable oil substitutes, olive oil is considered one of the healthiest options due to its high monounsaturated fat content and potential heart health benefits. Avocado oil and coconut oil are also healthy substitutes, each offering unique nutritional advantages for cooking and baking purposes.